One key debate many organizations face is:
Should we stick with manual coding or invest in automated code creation for our material master? Manual vs Automated Code Creation: Which One Ensures Better Data Accuracy?
For industries that manage thousands of items—like Oil & Gas, Manufacturing, EPC, and Healthcare—incorrect codes can result in poor procurement decisions, inflated inventory, and compliance risks.
This article explores the pros, cons, and ROI of both methods, with a focus on how automation, powered by AI/ML, is rapidly reshaping data accuracy across industries in India, the GCC, and the Far East.
What is Material Master Code Creation?
Material master coding refers to the process of assigning a unique identifier or classification (such as UNSPSC) to each item in your inventory or catalog. These codes are essential for:
- Standardizing data
- Facilitating global trade
- Ensuring seamless ERP integration (SAP, Oracle, Maximo)
- Improving procurement analytics
Manual Code Creation:
Historically, catalogers and procurement teams manually assigned codes to materials. While this method offers hands-on control, it’s prone to several challenges.
Why Manual Coding Falls Short
While manual coding may seem manageable at a small scale, it fails when:
- You manage over 50,000+ material SKUs
- You operate across multiple geographies and warehouses
- Your procurement teams rely on vendor-specific descriptions
Manual methods result in inconsistent nomenclature, wrong UOMs, and redundant codes — all of which cost money, time, and trust.
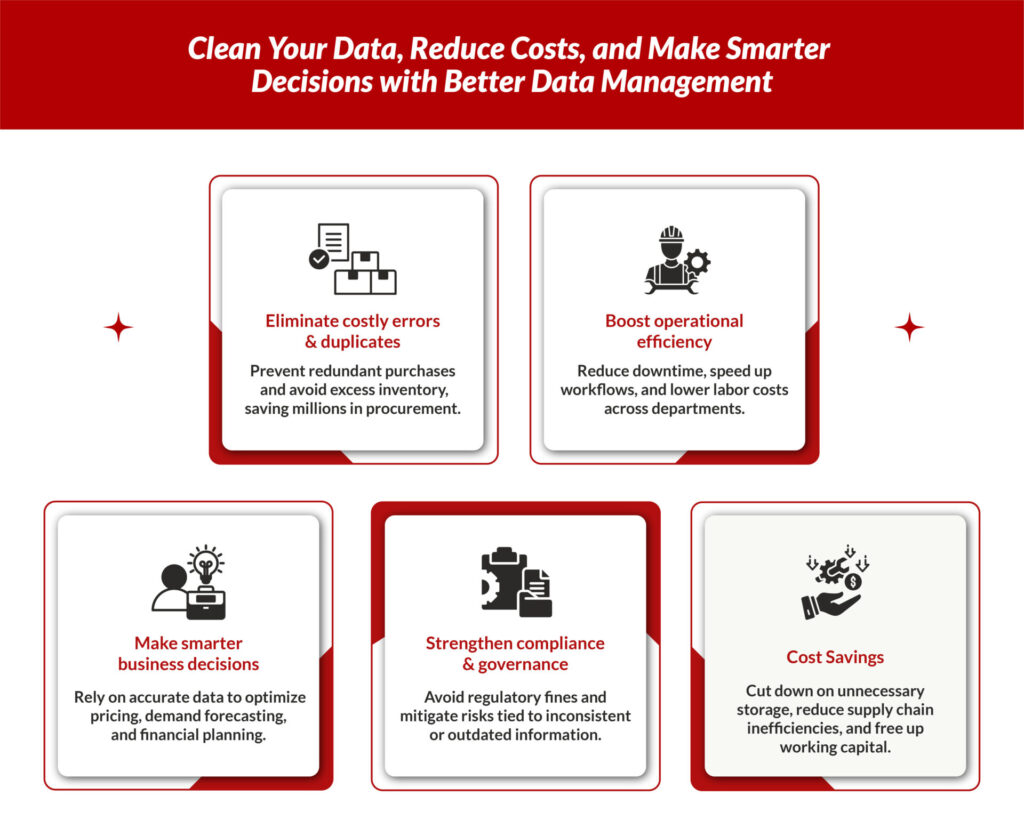
Common Pitfalls of Manual Code Creation
| Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| Human Error | Inconsistent classification and duplication |
| Time-Intensive | Slows down onboarding and catalog expansion |
| Poor Visibility | Lack of historical context or code logic |
| No Audit Trail | Difficult to track how or why a code was assigned |
| Dependency on Experts | Requires tribal knowledge, making it hard to scale |
Manual methods often lead to data silos, duplicated items, and incomplete records, especially when multiple teams are involved.
Ready to ditch the spreadsheets and drive accuracy with automation?
Book a free demo of Prosol today and see real-time AI-powered code generation in action.
Automated Code Creation:
With AI/ML-powered platforms like Prosol, organizations are shifting toward automated code creation for material master records.
Benefits of Automated Code Generation
- AI-based Code Assignment: Auto-generates the right UNSPSC or internal code by analyzing item descriptions and attributes
- Fuzzy Matching: Detects similar or duplicate items, minimizing redundancies
- Standardization at Scale: Ensures uniform naming conventions and classifications across locations and teams
- Speed: Codes thousands of records in hours—not weeks
- Audit-Ready: Transparent logs of each coding decision
- UOM Normalization: Automatically corrects mismatches in unit measurements
“Gartner reports that poor data quality costs organizations an average of $12.9 million annually.”
Source: Gartner Research
Manual vs. Automated Coding
Let’s consider a mid-sized manufacturing company in the GCC region managing 50,000 materials across multiple sites.
| Feature | Manual Coding | Automated Coding (via Prosol) |
|---|---|---|
| Time to Code 10,000 Items | 8-10 weeks | 3 days |
| Duplicate Rate | 18% | <2% |
| Classification Accuracy | ~70% | 98%+ |
| Audit Trail | Minimal | Full digital log |
| Resource Dependency | High | Low |
| Data Quality Score | 6/10 | 9.5/10 |
Outcome: By shifting to automated coding, the company saved ₹1.5 Crores in inventory costs within six months and reduced procurement lead times by 25%.
Industries Benefiting the Most
Industries with complex supply chains and massive inventories are seeing huge ROI from automation:
- Oil & Gas, Utilities, Marine & Ports: Accurate spare part codes reduce unplanned downtime.
- Manufacturing, EPC, Real Estate & Construction: Improved BOM integrity and vendor negotiations.
- Healthcare & Lifesciences: Eliminates life-critical errors from misclassified medical equipment.
- Banking, Government Entities, Defense: Ensures compliance with international procurement standards.
- Aviation & Engineering: Enhanced traceability and maintenance accuracy.
Why This Matters More in India, GCC, and Far East
These regions are experiencing rapid digital transformation, driven by infrastructure investment, regulatory modernization, and sustainability goals.
- GCC Vision 2030 is pushing public and private sectors to unify supply chains.
- India’s ‘Digital India’ Mission is encouraging industries to adopt smart MDM practices.
- Far East countries like Singapore and South Korea are leading the charge in AI adoption for asset and material management.
How to Get Started
If your team still relies on Excel sheets and manual coding processes, here’s how to transition:
- Audit Your Current Material Master
- Check for duplicates, inconsistent naming, and missing attributes.
- Choose the Right Tool
- Work with an AI-powered platform like Prosol that integrates with SAP, Oracle, or Maximo.
- Pilot with a Subset
- Test automation on 5,000–10,000 items and compare KPIs.
- Train Your Team
- Get your catalogers comfortable with automation and the in-built data dictionary.
- Scale Gradually
- Migrate site-by-site or business unit-wise for smoother implementation.
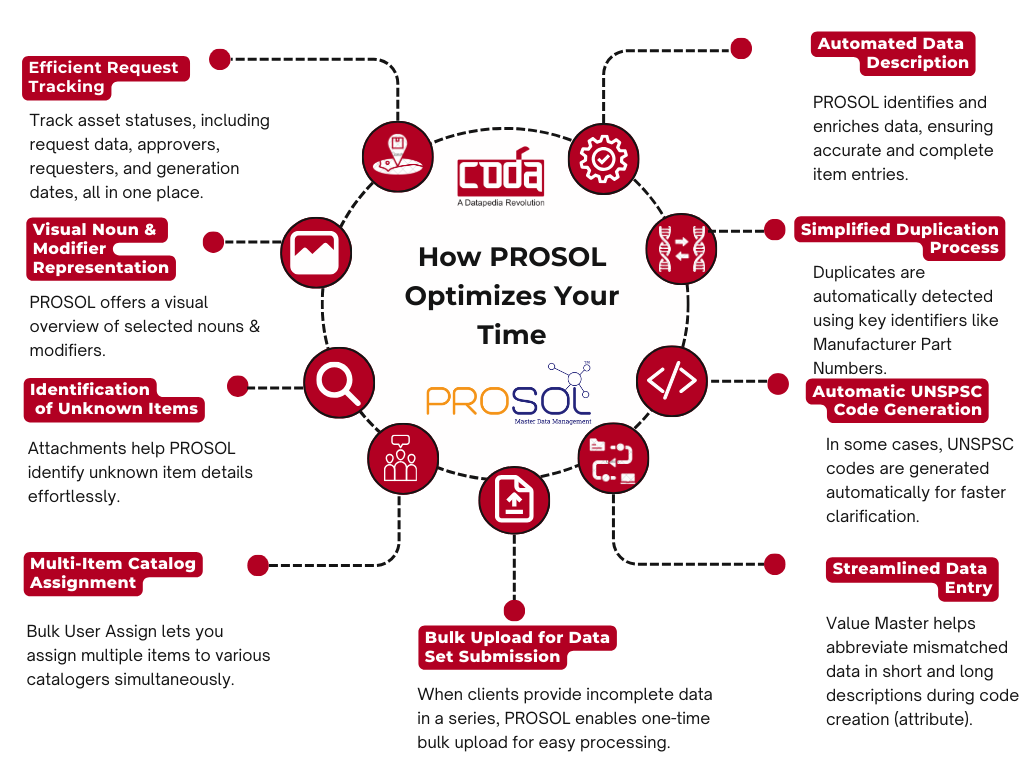
How Automated Code Creation Works in Prosol
- UNSPSC Code Generation: AI assigns correct UNSPSC codes automatically.
- Fuzzy Search: Detects and flags similar or duplicate materials during data entry.
- UOM Normalization: Standardizes units during data capture.
- Noun-Modifier Dictionary: Ensures consistent descriptors across all items.
- Image Matching: Visual validation with AI-assisted item images.
FAQ: Manual vs. Automated Code Creation
Q1: Can automated tools really understand complex material descriptions?
A: Yes. Tools like Prosol use Natural Language Processing (NLP) and AI-trained models to interpret complex descriptions and assign appropriate codes.
Q2: What if our data is messy or incomplete?
A: Prosol performs data cleansing and enrichment before assigning codes, so your data gets cleaned as it’s coded.
Q3: Is it secure to use an automated platform for critical data?
A: Yes. Enterprise-grade tools ensure data encryption, role-based access, and full audit trails to meet compliance standards.
Q4: How often do AI/ML models update their classification logic?
A: Most platforms, including Prosol, continuously learn and improve through user feedback and periodic model training.
Q5: Can Prosol handle industry-specific terminology?
A: Absolutely. Its noun-modifier dictionary is customizable, ensuring accurate contextual classification across industries like Oil & Gas, Healthcare, and EPC.
“An estimated 25% of material master data in large enterprises is either duplicated or outdated.” — McKinsey & Company
Source: McKinsey Digital Insights
Material/Item Coding Process Assessment Questionnaire
- Is your coding process standardized across all plants, departments, and geographies?
→ Lack of standardization often leads to duplicate entries and misclassified data. - How do you generate codes for new items—manually or through an automated system?
→ Manual processes can be slow, inconsistent, and error-prone. - Are you using a globally recognized classification system like UNSPSC or eClass?
- Is there a data dictionary or noun-modifier structure guiding the code creation process?
- How do you check for duplicates before creating a new material code?
→ If you’re not using intelligent tools (like fuzzy logic or AI), you’re likely missing duplicates. - Is your UOM (Unit of Measure) consistent across your material master?
- Do your material codes contain meaningful attributes (smart coding) or are they arbitrary?
- How long does it take to create and approve a new material code on average?
- Is your team aligned on naming conventions and description structures?
→ Misalignment here causes confusion and poor searchability. - How often do users struggle to find the correct material due to inconsistent descriptions or codes?
- Do you have a process to regularly audit and clean up your material master?
- Are item images or technical specs linked to the codes for better visibility?
- Can you easily track changes made to existing material codes and who made them?
- Are you capturing alternate part numbers, OEM references, or manufacturer details in your master?
- Is your current system integrated with your ERP, procurement, and inventory tools for real-time data flow?
Score:
You can rate each question on a scale of 1 (Not at all) to 5 (Fully optimized).
Use this to spot gaps in:
- Process efficiency
- Data consistency
- Duplication risks
- Integration with business systems
Conclusion
Manual coding had its time but in today’s high-speed, data-centric world, automated code creation for material master is the clear winner. From improving data accuracy and eliminating duplicates to reducing manual effort and driving digital transformation, automation is the future.
Whether you’re in India, the GCC, or the Far East, upgrading to an AI/ML-powered tool like Prosol can transform your entire data landscape—one accurate code at a time.
Automate your cataloging process with Prosol, our AI-powered tool trusted across industries.

Glossary for Material Coding & Master Data Management terms
UNSPSC (United Nations Standard Products and Services Code)
A globally recognized classification system used to categorize products and services. Helps in standardizing procurement and enabling spend analysis.
Smart Coding
The practice of generating item codes that carry embedded intelligence—such as category, specifications, or supplier—rather than arbitrary numeric codes.
Data Normalization
A process of organizing data to ensure consistency and compatibility. In master data, this means using standard formats, units, and structures across all records.
Fuzzy Matching
An AI-powered technique that detects near-duplicates or similar items in your database, even if names or spellings differ slightly.
Code Taxonomy
A structured hierarchy or classification system that defines how items should be grouped, named, and categorized—essential for scalable data governance.
Noun Modifier Dictionary
A controlled vocabulary used during item description to ensure uniformity (e.g., using “Pump, Centrifugal” vs. “Centrifugal Pump”).
Unit of Measure (UOM)
The standard unit used to quantify materials—like kg, liter, meter. UOM standardization is key to avoiding inventory mismatches and procurement errors.
Golden Record
The most accurate, complete, and reliable version of a data entity. In material master data, it eliminates duplicates and inconsistencies.
Data Deduplication
The process of identifying and eliminating duplicate records in the master database to reduce waste, confusion, and inefficiency.
Cataloging Tool
Software used to create, maintain, and standardize item master data—often includes features like auto-coding, image management, and validation checks.
Master Data Governance
A set of policies, processes, and tools to ensure the accuracy, consistency, and accountability of master data across the enterprise.


